Common air purification sizing metrics and how they’re related to each other are discussed below:
Room Area (Square Feet)Room area is often measured in Square Feet (sq.ft.) and some products describe their performance using this metric. Knowing what room area (sq.ft.) needs to be treated and how many air changes (ACH) are desired allows for CFM to be calculated and the properly sized products to be determined.
Air Changes per Hour (ACH)ACH is short for air changes per hour and describes how many times, during one hour, the volume of air from a space is replaced with purified air. The term "purified air" typically refers to outdoor air, but purifying existing indoor air through proper filtration (minimum MERV 13) and supplementary technologies (UVC light and Bipolar Ionization) has been found to have similar benefits as outdoor air1 with reduced energy cost because the air has already been conditioned. It is important to note that at this time filtered indoor air does not replace outdoor air requirements, but in regards to dilution and purification of airborne pathogens it has an equivalent effect. A simple formula for determining ACH is provided below:
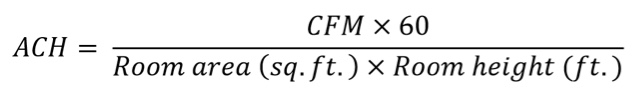 Air Volume Rate (CFM)
Air Volume Rate (CFM)
CFM is short for cubic feet per minute and is the industry standard for describing how much air HVAC air distribution products provide. Most air purifiers provide a range of CFM and it’s important to understand where a device is operating within this range since it can impact sound and airspeed levels, and therefore occupant comfort. CFM is the most transparent performance metric because it is a stand-alone value that does not rely on other variables or assumptions while other performance metrics (like CADR and room size) do.
Knowing what room area (sq.ft.) needs to be treated and how many air changes (ACH) are desired allows for CFM to be determined. For example, to achieve 2 ACH from an air purifier in a room with 9ft ceiling height, the air purifier's flow rate is:
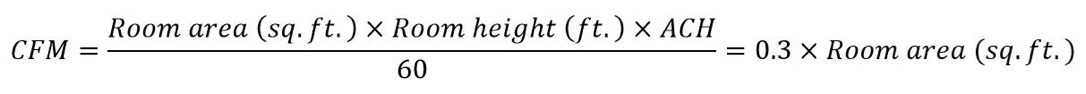
ASHRAE2 and other organizations3 often recommend that ACH be higher than 2, but air purification devices typically run separately from building comfort cooling, which means the total ACH of the space will be higher.
Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR)CADR is short for Clean Air Delivery Rate and represents the volume of filtered air measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). This term comes from AHAM (Association of Home Appliance Manufacturers) and describes a purifier’s ability to remove three different sizes of particles:
- Small = Smoke CADR (0.09 – 1 micron)
- Medium = Dust CADR (0.5 – 3 microns)
- Large = Pollen CADR (5 – 11 microns)
Smoke CADR is recommended to calculate room area (square feet) because it’s often the lowest score since smoke particles are the smallest of the three.
CADR is based on an air purifier running at the highest (maximum) fan speed, which can be misleading since occupants often do not run air purifiers at the “high” setting due to disruptive noise or airflow. As a result, it’s important to quantify what CFM the CADR is based on otherwise it’s easy to assume a higher CADR than what is actually achieved.
Converting CADR to CFM is straight forward. If the air purifier filter removes 90% of particles (efficiency) and the unit can push 100 CFM, then the CADR for the air purifier is 100 CFM x 0.9 = 90 CADR. True HEPA filters have a 99.97% efficiency at 0.3 microns, their most penetrating particle size. Therefore, using these filters results in CADR and CFM being effectively equivalent. Many air purifiers do not use true HEPA filters and as a result there is some loss from lower efficiency and a conversion is needed. Airflow output can change over time as the filter loads (collects contaminants) and filter pressure increases, which should be considered. Price products ensure constant performance by changing motor speed as required.
2 - ASHRAE Epidemic Task Force Document
3 - Harvard 5-step guide to checking ventilation rates in classrooms
